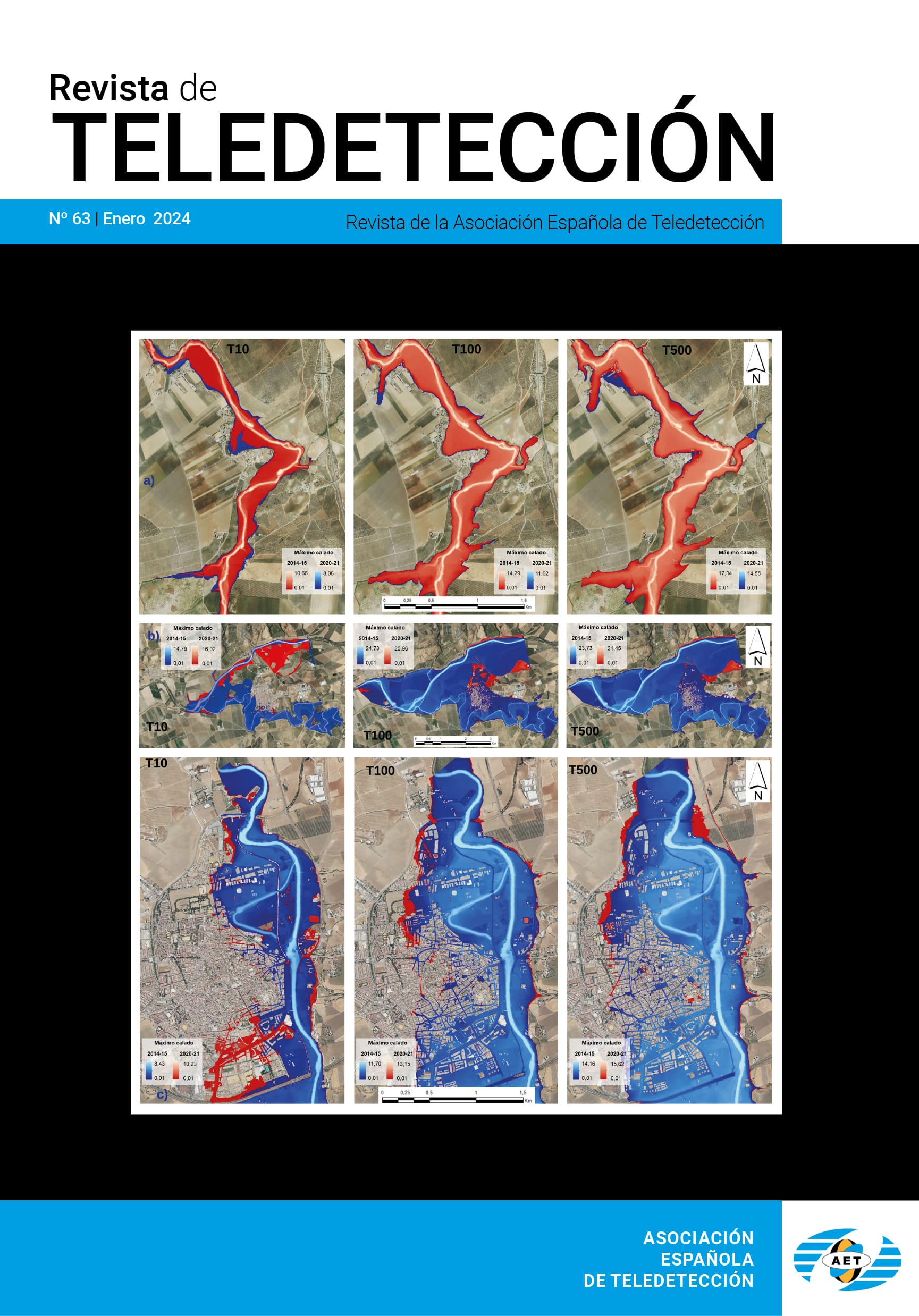
Determinación del nivel freático del agua subterránea de una isla mediante imágenes del altímetro ASTER
E. Caselles (eduardo.caselles@uv.es)
C. Pitarch y V. Caselles
RESUMEN
Para determinar el nivel freático del agua subterránea se usan, normalmente, medidas tomadas desde avión, determinaciones mediante resistímetros o realizando perforaciones. Esta forma de proceder requiere, aproximadamente, la toma de una muestra por hectárea, lo que alarga y encarece considerablemente este tipo de estudios. Sin embargo, la teledetección espacial constituye una herramienta ideal para determinar el nivel freático del agua subterránea. Así, en este trabajo, hemos utilizado las medidas obtenidas por el altímetro del satélite ASTER. El nivel freático del agua subterránea de una isla viene determinado, de forma aproximada, por la diferencia entre el nivel de cada punto de la isla y el que tenga el agua del río en ese momento. Así, el nivel freático del agua subterránea de una isla será, por tanto, variable a lo largo del año. Como zona de estudio hemos elegido una isla del Danubio, situada en las proximidades de la población de Roseti, en el partido judicial de Calarasi, en Rumania. Las coordenadas geográficas de la isla son: entre 44° 07’ y 44° 13’ de latitud Norte y entre 27° 19’ y 27° 34’ de longitud Este. El nivel freático del agua subterránea para la zona de estudio, determinado el 30 de junio de 2008, resultó tener un valor variable entre 1 y 8 m. Estos resultados se validaron mediante un mapa topográfico de la zona y la toma de muestras «in situ» en los diferentes pozos de la isla. El RMS resultante fue de 1 m..
Palabras Clave:nivel freático, agua subterránea, altímetro, ASTER, isla, Danubio.
ABSTRACT
To determine the water table depth it can be normally used airborne measurements, resistimeters determinations or perforation analyses. This way of procedure requires, approximately, taking a sample per hectare, which is expensive and time-consuming. However, remote sensing constitutes an ideal tool for determining water table depth. Then, in this work we have used the measurements carried out by the altimeter of ASTER satellite. The water table depth of an island can be approximately determined by means of the difference between the altitude of each point in the island and the altitude of the river in this moment. So, the water table depth of an island is variable trough the year. As study area we have selected an island of the Danube, located near the Roseti village, Calarasi district, in Romania. The geographical coordinates of the island are: between 44° 07’ and 44° 13’ N latitude and between 44° 07’ and 44° 13’ E longitude. The water table depth, measured on 30 June, 2008, was variable between 1 and 8 m. These results were validated using a topographical map of the area and taking some in situ samples at the island wells. An RMS of 1 m was obtained
KEYWORDS: water table depth, ground water, altimeter, ASTER, island, Danube.
PULSE AQUI PARA DESCARGAR EL ARTÍCULO COMPLETO