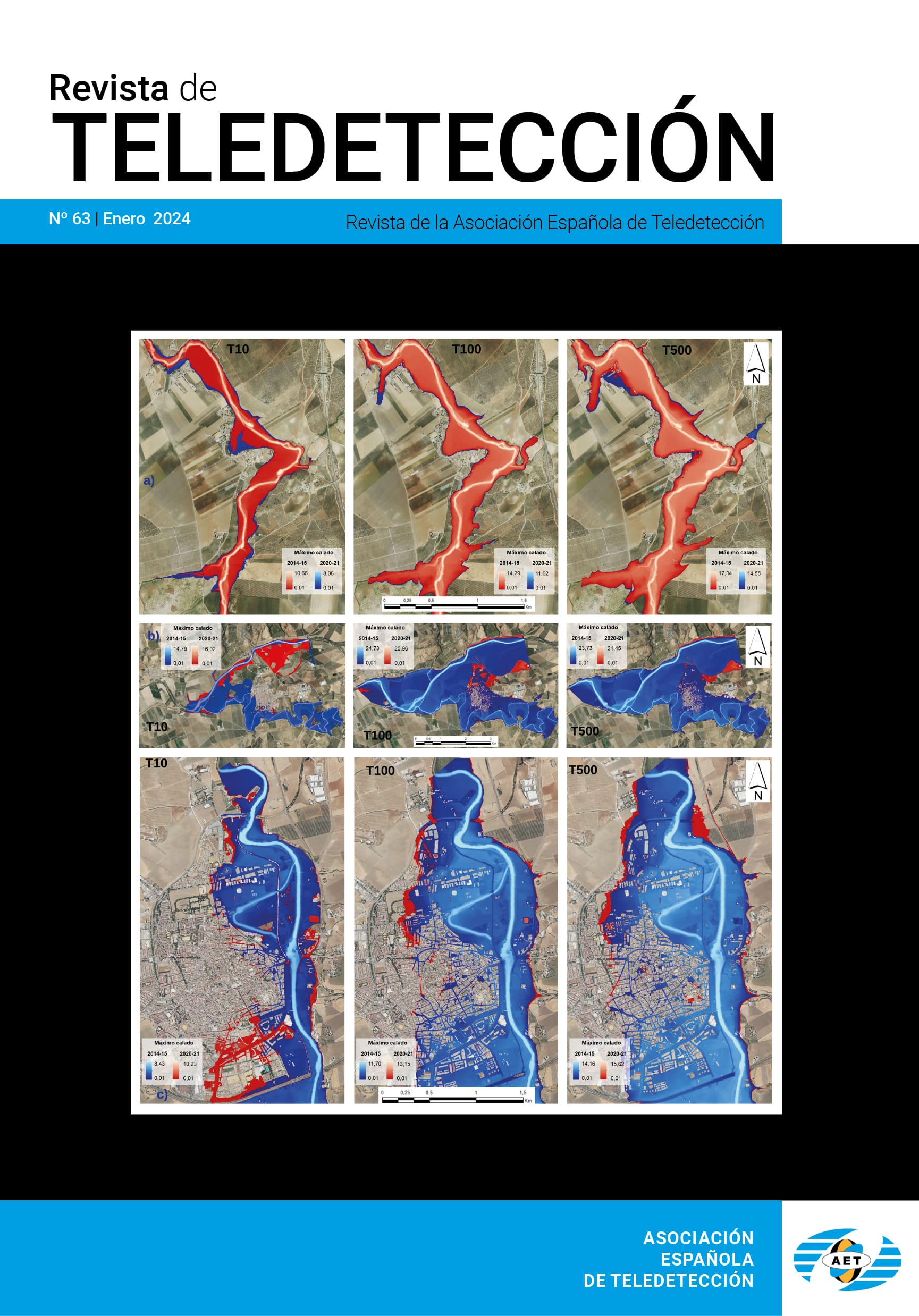
Dinámica estacional e interanual del NDVI en bosques nativos de zonas áridas argentinas
M. R. Iglesias (charo@agro.unc.edu.ar)
A. Barchuk y M. P. Grilli
RESUMEN
Dinámica estacional e interanual del NDVI en bosques nativos de zonas áridas de Argentina. Se analizó la dinámica estacional e interanual de la actividad fotosintética de la vegetación original y su relación con las lluvias, en tres Reservas Naturales con diferentes regímenes hídricos. Se empleó el Índice Verde Normalizado (NDVI-Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) de imágenes de cada diez días del satélite
SPOT V en un período de cinco años (1998- 2003). La relación entre el NDVI y las lluvias se realizó por medio de correlaciones cruzadas. El análisis de las variaciones interanual y estacional del NDVI, permitió obtener valores de referencia del patrón de crecimiento vegetal en cada Reserva. Las variaciones del NDVI en el tiempo de las tres áreas protegidas evidencian el comportamiento estacional de la vegetación. Los valores de los atributos del NDVI son mayores en la Reserva más húmeda. Por otro lado, el análisis de correlaciones cruzadas comprueba que existe una correlación entre los valores de precipitaciones y el NDVI y en general, esta es mayor cuando se lo relaciona con un mes de retraso de la respuesta de la vegetación con respecto a las lluvias ocurridas.
PALABRAS CLAVE: Índice de Verde Normalizado (NDVI), correlaciones cruzadas, precipitaciones, bosques xerofíticos, Chaco Árido, Provincia fitogeográfica de Monte.
ABSTRACT
Seasonal and interannual dynamics of NDVI in dry forests of Argentina. The seasonal and interannual dynamics of the photosynthetic activity of the original vegetation and the relationship with the rainfall in three Forest Reserves were analyzed. It was used the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) of the first 10-days image of SPOT V satellite along f ive years (1998-2003). For the study of the relationship between NDVI and rainfall, cross correlation was applied. The analysis of interannual and seasonal variations of NDVI shows reference values of patterns of plants growth in each Reserve.
The NDVI variations over time in the three protected areas show the seasonal dynamic of native vegetation. The values of the NDVI`s attributes are bigger in the wetter Reserve. Furthermore, cross correlation analysis shows that there is a correlation between the values of rainfall and NDVI, and this is bigger when it is related to one month of the response of NDVI from the rainfall occurring.
KEYWORDS: Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), cross correlation, rainfall, xerofitic forest, Monte, Arid Chaco
PULSE AQUI PARA DESCARGAR EL ARTÍCULO COMPLETO