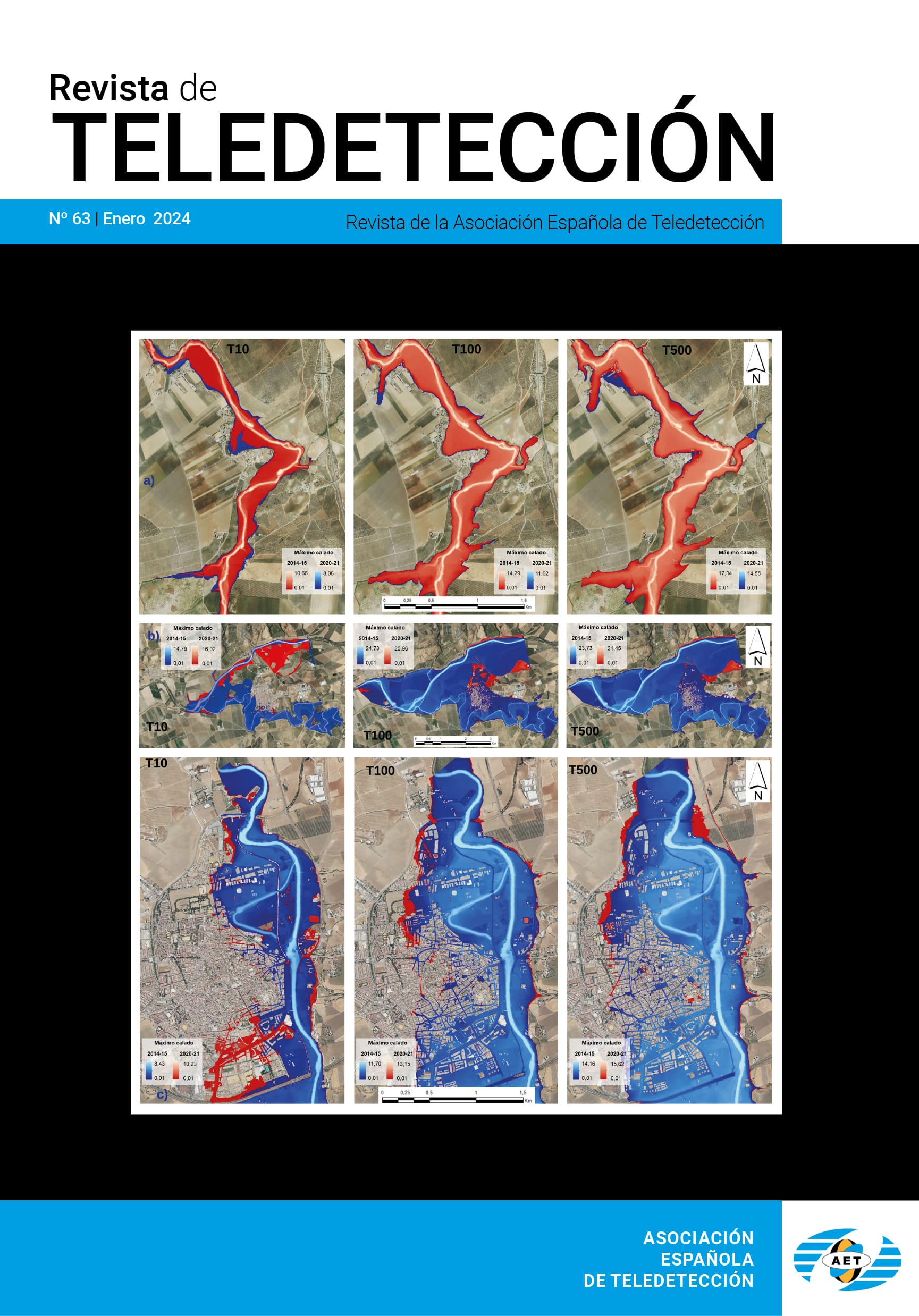
Sistema de información geográfica agrometeorológico para el seguimiento de la vegetación en Castilla y León: diseño y...
...primeras aplicaciones.
P. Illera, J. A. Delgado, A. A. Femández-Manso yA. Femández-Unzueta
RESUMEN
En el trabajo presentamos el diseño y algunas aplicaciones del Sistema de Información Geográfica Agrometeorológico desarrollado en el LATUV con objeto de llevar a cabo un seguimiento de la vegetación en Castilla y León. Su primera fuente de información es la Teledetección: imágenes Meteosat y NOAA que recibimos y procesamos diaria-mente mediante los equipos instalados en el LATUV. El canal visible de las imágenes Meteosat nos permite calcular la radiación solar global; las imágenes NOAA-AVHRR se utilizan para calcular el índice de vegetación NDVI y la temperatura del suelo. En el SIG hemos integrado también datos de la red de estaciones termopluviométricas del Instituto Nacional de Meteorología en la que se miden temperatura del aire y precipitación. Estos datos se han interpolado a la resolución espacial de las imágenes A VHRR. Por último, hemos incluido la cartografía digital CORINE. El SIG se está aplicando para llevar a cabo estudios de vegetación siguiendo tres líneas: estimación de rendimientos de cosechas de cereal, vigilancia de zonas foresta-les y estimación del peligro de incendios forestales debido al estrés hídrico de la vegetación. En este trabajo presentamos las dos primeras.
PALABRAS CLAVE: Teledetección y SIG, Agrometeorología, NDVI, Aplicaciones Agroforestales.
ABSTRACT
In this paper we present fue design and some results of fue GIS developed in OUT Remote Sens-ing Laboratory to be used for vegetation monitoring in the region of Castilla y León. The first source of information is Remote Sensing: Meteosat and NOAA-AVHRR images received and processed daily in OUT laboratory. Meteosat visible images allow for the calculation of global solar radiation; NOAA-AVHRR data are used to calculate both the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and surface temperatures. The system includes meteorological data provided by the Spanish Meteorological Institute (INM). Air temperature and rainfall recorded by the regional network have been available and then interpolated to the AVHRR images spatial resolution. Finally, digital vegetation mapping derived from the CORINE land cover program has algo been used. The system is being applied for vegetation monitoring following three lines: cereal crop yield estimation, monitoring of forest areas and estimation of the forest rife danger due to hydric stress of the vegetation. Here, the two first applications are presented.
KEY WORDS: Remote Sensing and GIS, Agrometeorology, NDVI, Agricultura! and For-estry Applications.
PULSE AQUI PARA DESCARGAR EL ARTÍCULO COMPLETO.